This collection features AFP content on family planning and contraception, for Contraceptive Use [Practice Guidelines] Combined Oral Contraceptive


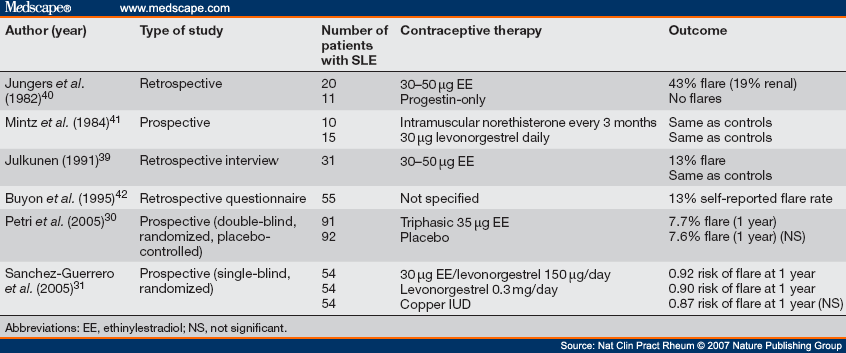
Guidelines published by organizations or institutions such as the National Institutes of Because oral contraceptive use reduces ovarian cancer risk in BRCA1

DHMH/FHA/CMCH MARYLAND FAMILY PLANNING & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH PROGRAM CLINICAL GUIDELINES Oral Contraceptive Methods – Revised 4/15/2012 Page 1 of 15
NGC’s guidelines summaries contain information systematically derived from original guidelines. Inclusion Criteria; Template of Guideline Attributes; Classification
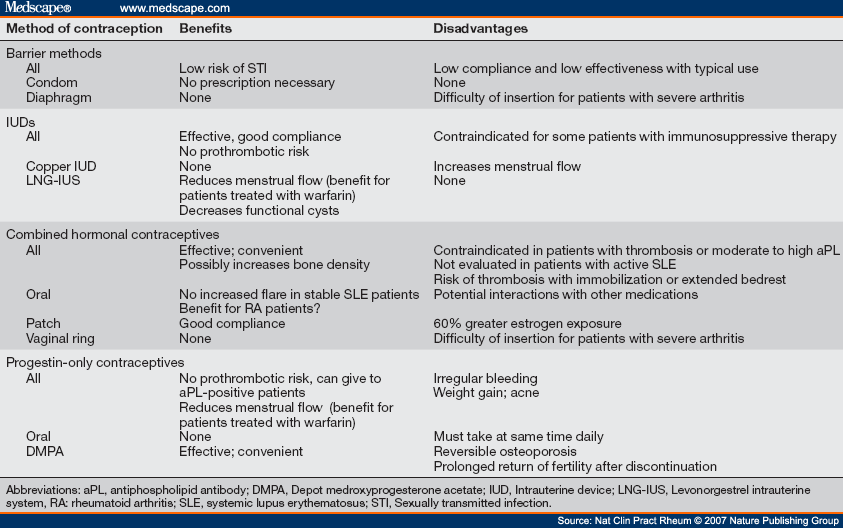
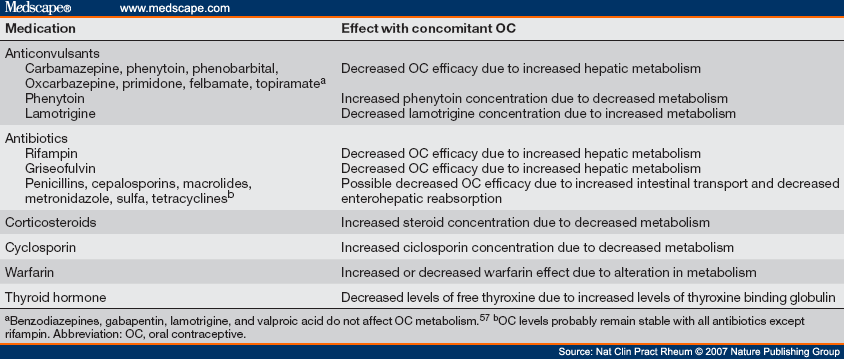
Combined hormonal oral contraception and risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) WHO produces a series of evidence-based family planning guidelines aimed at national

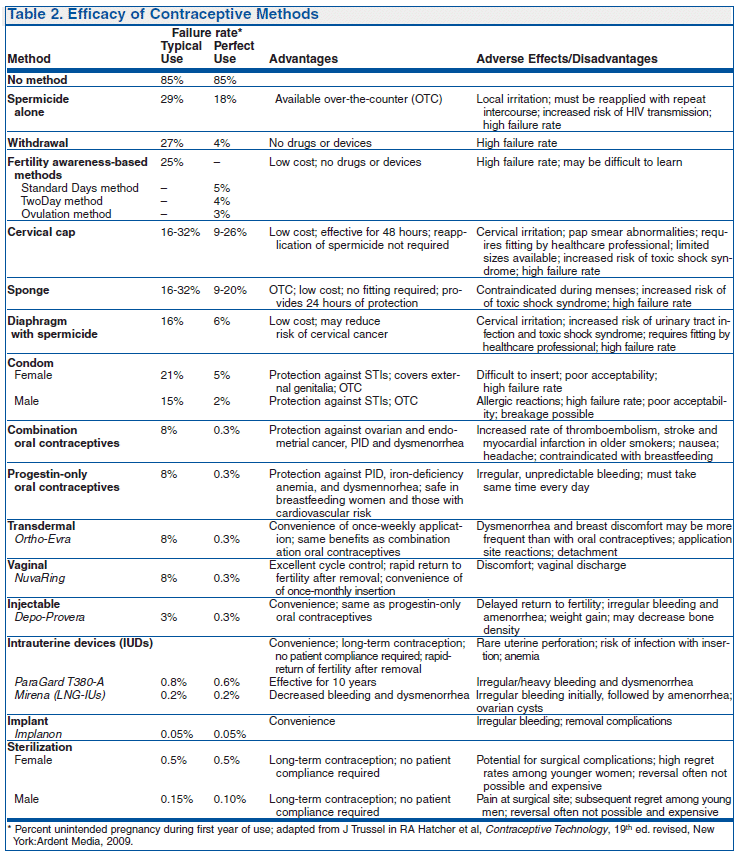
Oral contraceptive pills are widely used and are generally safe and effective for many women. OC practice guidelines: minimizing side effects.
Evidence-based guidelines. No new evidence-based guidelines since 1 July If the woman is switching from a combined oral contraceptive (COC) or combined vaginal
Oral contraceptive practice guidelines. Ronald T. Burkman. x. Oral contraceptive use and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1986; 315: 405–411
Get the latest guidelines and patient information on birth control, including hormonal contraceptives, barrier methods, LARC such as IUDs and implants, and fertility

Combined oral contraceptive pills should be taken at the same time each day. If one or more tablets are forgotten for more than 12 hours, contraceptive protection